Crosslinker phenolic “immunoaffinity columns” are finally here, and say goodbye to traditional SPEs!
Our self-developed cross-streptolysin immunoaffinity columns are now on the market, which can replace the traditional SPE method with complicated operation, high reagent loss and high contamination, and realize the effective purification of complex matrices, which can significantly improve the accuracy and reproducibility of the test, and is suitable for a wide range of matrices. Let’s review about Streptozotocin (Streptozotocin)!
01 Types
At present, more than 70 types of Streptomyces toxins (alternariol toxins) and their derivatives have been identified, including Alternariol (AOH), Alternariol monomethyl ether (AME), Tenuazonic acid (TeA), Tenotoxin (TEN), etc. Among them, TeA is the only nitrogen-containing compound, which is recognized as the most toxic Streptomyces toxin. Tenotoxin (TEN), etc. Among them, TeA is the only nitrogen-containing compound, which is recognized as the most toxic mycotoxin.
02 Pollution risk
Streptomyces mycotoxins are widely present in a wide range of foods, especially in cereals, fruits and vegetables. Examples include wheat, corn, tomatoes and their products. Among them, TeA has the highest detection rate, followed by AOH and AME.The level of streptogrammatoxin contamination in food varies depending on factors such as region, climatic conditions, type of food, and storage methods.
03 Toxicity and Risks
These toxins have a wide range of toxic effects, including endocrine disruption, genotoxicity, cytotoxicity, acute toxicity and even carcinogenicity. Humans may be exposed to these toxins through the consumption of contaminated food, and long-term exposure may result in health effects.
04 Standard Regulations
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has provided a scientific opinion on the public health risk associated with streptozotocin in food and has set a threshold of toxicological concern (TTC).
Currently (as of June 2024) there are a number of testing standards in the country: including one entry/exit standard, one local standard, and four group standards.
05 Preventive and control measures
To reduce the hazard of Streptomyces toxins, researchers have explored a variety of methods, including physical controls (e.g., high-temperature treatment, radiation), chemical controls (e.g., use of biocides), biological controls (e.g., use of antagonistic microorganisms), and biodegradation methods.
06 Detection Methods
The current standards mostly use liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), which is widely used in the quantitative analysis of streptozotocin in food because of its high sensitivity and high selectivity. Other detection methods include high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Sample pretreatment methods include: solid phase extraction (SPE) hair, QuEChERs method, which is currently the most applied, and also dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME), molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction (MIP-SPE), direct extraction and dilution, low-temperature freezing method, n-hexane liquid-liquid partitioning and other purification methods in the literature for the removal of weakly polar impurities from the samples.
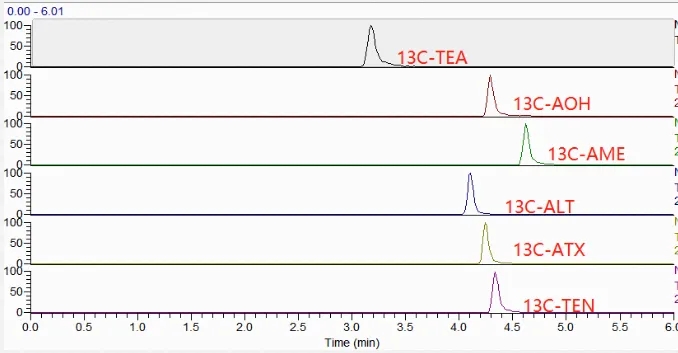
Our company can provide Streptomyces toxin internal and external standard single standard and mixed standard, and has assisted customers to establish the detection method for this kind of toxin many times. Matching multi-functional clean-up column, simplify the operation compared with conventional solid phase extraction, one-step method to complete the clean-up in 30S. Immunoaffinity columns have been developed and marketed, welcome to contact us for trial!